Types of solar-related projects in the Center:
- Solar fuels;
- Solar hydrogen;
- Dye-sensitized solar cell;s
- Nanowire solar cells;
- Organic photovoltaics;
- Strain-tuning of semiconductor properties;
- Non-focusing concentrator optics;
- Plasmonic nanostructures;
- Mechanisms of electron, proton, and energy transfer;
- Artificial photosynthesis;
- Tandem solar cells;
- Heterojunction solar cells;
- Photocatalytic conversion of CO2 to hydrocarbon fuels.
Select research publications:
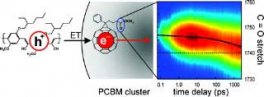
 Bimolecular charge recombination is examined in a polymer blend photovoltaic material using time-resolved vibrational spectroscopy on the 100 fs to millisecond time scales.
Bimolecular charge recombination is examined in a polymer blend photovoltaic material using time-resolved vibrational spectroscopy on the 100 fs to millisecond time scales.
Ryan D. Pensack, Kyle M. Banyas and John B. Asbury, Charge Trapping in Organic Photovoltaic Materials Examined with Time-Resolved Vibrational Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2010, 114, pp 5344-5350.
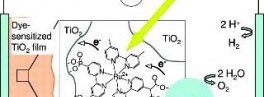
High rate conversion of CO2 and water vapor is achieved using copper sensitized titania nanotube arrays under outdoor sunlight.
Proton-coupled electron transfer (PCET) reactions play an essential role in a broad range of energy conversion processes, including photosynthesis and respiration. These reactions also form the basis of many types of solar fuel cells and electrochemical devices. Recent advances in the theory of PCET enable the prediction of the impact of system properties on the reaction rates. These predictions may guide the design of more efficient catalysts for energy production, including those based on artificial photosynthesis and solar energy conversion.
 S. Hammes-Schiffer, Theory of Proton-Coupled Electron Transfer in Energy Conversion Processes. Acc. Chem. Res., 2009, 42, pp 1881-1889
S. Hammes-Schiffer, Theory of Proton-Coupled Electron Transfer in Energy Conversion Processes. Acc. Chem. Res., 2009, 42, pp 1881-1889
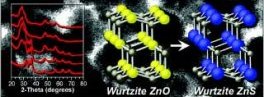
The controllable synthesis of semiconductor nanocrystals is important for exploiting their size-dependent properties in a variety of applications. Through careful mechanistic studies, we show that ZnO nanoparticles, which adopt the WZ structure, form as intermediates in typical reactions that generate WZ-ZnS. This implies that ZnO nanoparticles can serve as structural templates for the preferential formation of WZ-ZnS nanoparticles, and this is confirmed experimentally. Similar chemistry can be used to preferentially form WZ-ZnSe and ZB-ZnSe.
F. Dawood and R. E. Schaak, ZnO-Templated Synthesis of Wurtzite-Type ZnS and ZnSe Nanoparticles J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, pp 424-425.