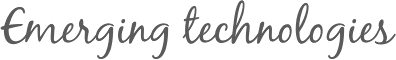 We have heard about them a lot in medias, we are told they are the future, yet no one has ever seen them so far. Of course, how could one? Their size is about one ten thousandth of a width a single human hair or less and surprisingly, they are called nanomaterials.
We have heard about them a lot in medias, we are told they are the future, yet no one has ever seen them so far. Of course, how could one? Their size is about one ten thousandth of a width a single human hair or less and surprisingly, they are called nanomaterials.
We are said they have unique properties, for example: capability of bearing extreme weights as for ropes, impenetrability for water or other small particles like germs as for clothes or superior use as containers for conducting a wide variety of experiments as for science.
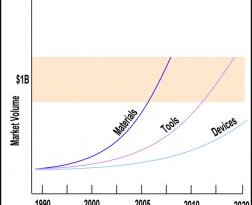
In the picture: Some of commonly used nanomaterials.
We have to admit, that opportunities what-to-do with these materials are really amazing. They are used in almost every field of industry. Here are some interesting aplication:
 a) Medicine - absorption ability of nanomaterials is tested to treat cancer diseases. They are also used as vessels to deliver a medicament into demanded destination without interacting with body imunity elsewhere.
a) Medicine - absorption ability of nanomaterials is tested to treat cancer diseases. They are also used as vessels to deliver a medicament into demanded destination without interacting with body imunity elsewhere.
Nanorobots are developed for surgery without a regular need for an incision.
b) Food production - Marks on food to secure the knowledge of their origin. Means of fighting microorganisms.
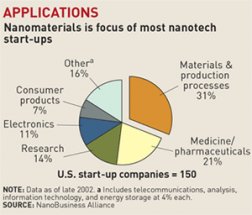 c) Electronics - Extremely big memory carriers in a small size. Display devices superb in quality of the image.
c) Electronics - Extremely big memory carriers in a small size. Display devices superb in quality of the image.
d) Engineering - Very durable materials with low friction and extreme persistence against water.
e) Space shuttles - Materials for satellites, developments of new fuel cells.
It is no secret that for the last year the nanotechnology market made 225 billions USD in sales.
However, do we really understand these nanomaterials? First vital thing to be aware of: In the world of the smallest particles the physical rules, as we know them, are not applied. When we reach the size of single molecules, particles cease to behave as would react their counterparts in the macroscopic world. They bend light, non-conducting materials start to conduct electricity and much more. These phenomena are under scrupulous research in a branch of science called: quantum physics.
See also:- progetto per investitori privati Bit Gpt feedback degli investitori