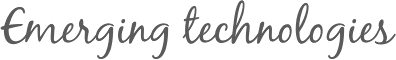
Abstract:
Nanocomposites are becoming an ever increasingly important material for various products. Their size gives them unique structural, thermal, and conductive properties versus traditional composites. Nanocomposites are being developed to deliver drugs, function as new flexible batteries, and as the next generation of building materials. Nanocomposites can be tailored to work for certain applications and materials, and when incorporated into porous materials they gain additional properties. The research presented below has many similarities in the area and approach, and it is argued that there needs to be a more diverse range of investigation in order to further this promising composite.
Introduction:
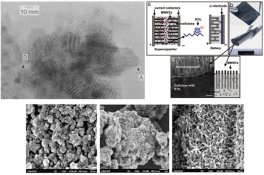
Nanocomposites, although highly technical sounding, have been around since the time of the Maya civilization, who inhabited Central America. Nanocomposites are, as the term suggests, composite materials containing nanosized (n, 10^-9) particles [12]. Composites, as a reference, are mixtures of several materials which give the final product characteristics of all the mixed materials. Basic examples of composites include wood, mud and straw, bone, etc [10]. Nanocomposites have gained popularity in recent years due to their unique characteristics. However, evidence of basic nanocomposites can be traced back to just several hundred years AD during the time of the Maya. The Maya people created a blue paint from local clays and other organic products which resist acids, heat, and aging [11].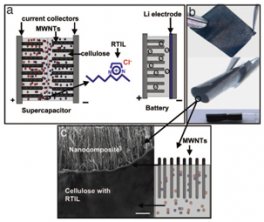 1) inside its matrix which gave it these characteristics [11]. While this example of a nanocomposite was not one which was created intentionally, nanocomposites of various types are readily being created in labs and industrial settings for a multitude of applications. This review will compare and contrast the various common types of nanocomposites being created and postulate on the future of this material technology.
1) inside its matrix which gave it these characteristics [11]. While this example of a nanocomposite was not one which was created intentionally, nanocomposites of various types are readily being created in labs and industrial settings for a multitude of applications. This review will compare and contrast the various common types of nanocomposites being created and postulate on the future of this material technology.
The rapidly expanding field of Biomedical Engineering has begun to incorporate nanocomposites for use, often temporarily, as bone and tissue replacements [5, 7]. These materials often adopt the name, bionanocomposites and differ from traditional uses for nanocomposites in a specific way. The nature of human bone and tissue regeneration requires a nanocomposite that biodegrades over time, and allows the patients’ own system to take over. In addition, these nanocomposites must be biocompatible with the human body, thus creating no undesired reactions or interactions [7].