 Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Northern Illinois University, DeKalb, Illinois 60115, Materials Science Division, Argonne National Laboratory, Argonne, Illinois 60439, Advance Photon Source, Argonne National Laboratory, Argonne, Illinois 60439, Department of Physics, Northern Illinois University, DeKalb, Illinois 60115
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Northern Illinois University, DeKalb, Illinois 60115, Materials Science Division, Argonne National Laboratory, Argonne, Illinois 60439, Advance Photon Source, Argonne National Laboratory, Argonne, Illinois 60439, Department of Physics, Northern Illinois University, DeKalb, Illinois 60115
J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132 (7), pp 2151–2153
DOI: 10.1021/ja909442c
txu@niu.edu, †
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Northern Illinois University.
, ‡Materials Science Division, Argonne National Laboratory.
, §Advance Photon Source, Argonne National Laboratory.
,Department of Physics, Northern Illinois University.
Section:Abstract
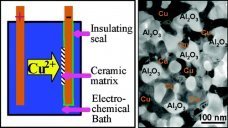
Platinum nanoparticle catalysts are essential for achieving energy-efficient and greener chemical processes that involve breaking or establishing of H−H, C−H, or O−H bonds. In this work, we report an innovative top-down strategy to prepare the supported Pt nanoparticles with an average size of 2 nm, starting directly from bulk metallic Pt by metallurgical method. Bulk platinum was dissolved in liquid lithium and ruptured into nanoparticles. This Li−Pt liquid alloy was quenched into Li−Pt solid solution. The lithium content was further converted into LiOH. The resulting powder of Pt nanoparticles in LiOH can be mixed with any nonaqueous support materials. Thereafter, the LiOH can be selectively leached off by water, allowing Pt nanoparticles to be adsorbed on the desired support material. Transmission electron microscope and extended X-ray absorption fine structure analyses demonstrated that the as-formed Pt nanoparticles have an average size of around 2 nm. The carbon-supported Pt nanoparticles prepared by this method inherit more characteristics of their bulk counterparts so that high specific catalytic activity of bulk Pt is maintained, which is confirmed by a preliminary electrocatalytic characterization of oxygen reduction reaction (ORR).
Citing Articles
Citation data is made available by participants in CrossRef's Cited-by Linking service. For a more comprehensive list of citations to this article, users are encouraged to perform a search in SciFinder.
This article has been cited by 1 ACS Journal articles (1 most recent appear below).
- Chi-Kai Lin, Yan-Gu Lin, Tianpin Wu, Heather M. Barkholtz, Qiyin Lin, Haojuan Wei, Dale L. Brewe, Jeffrey T. Miller, Di-Jia Liu, Yang Ren, Yasuo Ito, and Tao Xu
Inorganic Chemistry2012 51 (24), 8
-
Direct Synthesis of Bimetallic Pd3Ag Nanoalloys from Bulk Pd3Ag Alloy
Chi-Kai Lin, Yan-Gu Lin, Tianpin Wu, Heather M. Barkholtz, Qiyin Lin, Haojuan Wei, Dale L. Brewe, Jeffrey T. Miller, Di-Jia Liu, Yang Ren, Yasuo Ito, and Tao Xu
We report a transformative, all inorganic synthesis method of preparing supported bimetallic Pd3Ag alloy nanoparticles. The method involves breaking down bulk Pd3Ag alloy into the nanoparticles in liquid lithium, converting metallic Li to LiOH, and ...

 Because I believe
Because I believe  One who loves God will see what they believe and the ones who trust science will believe what they see
One who loves God will see what they believe and the ones who trust science will believe what they see



